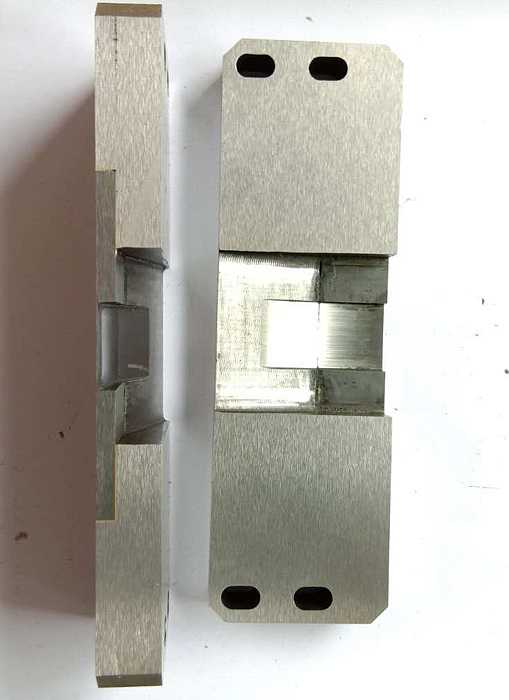
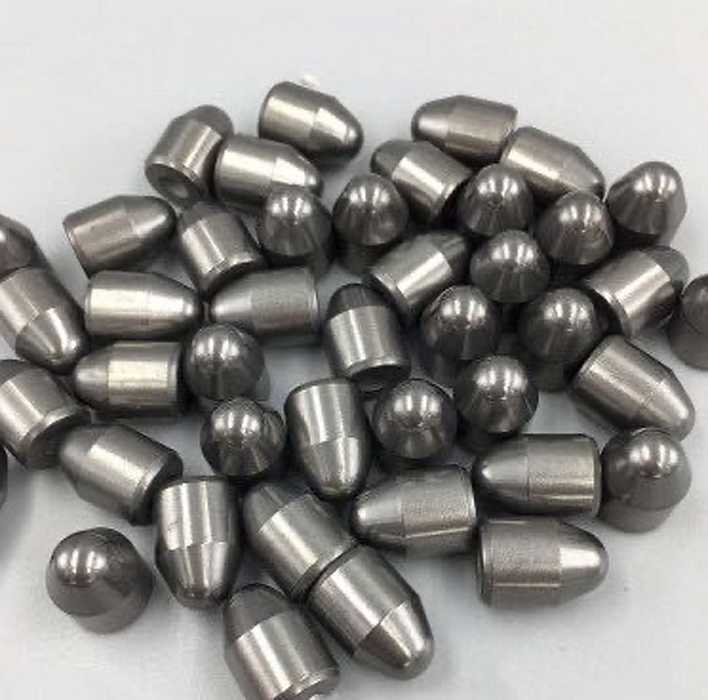
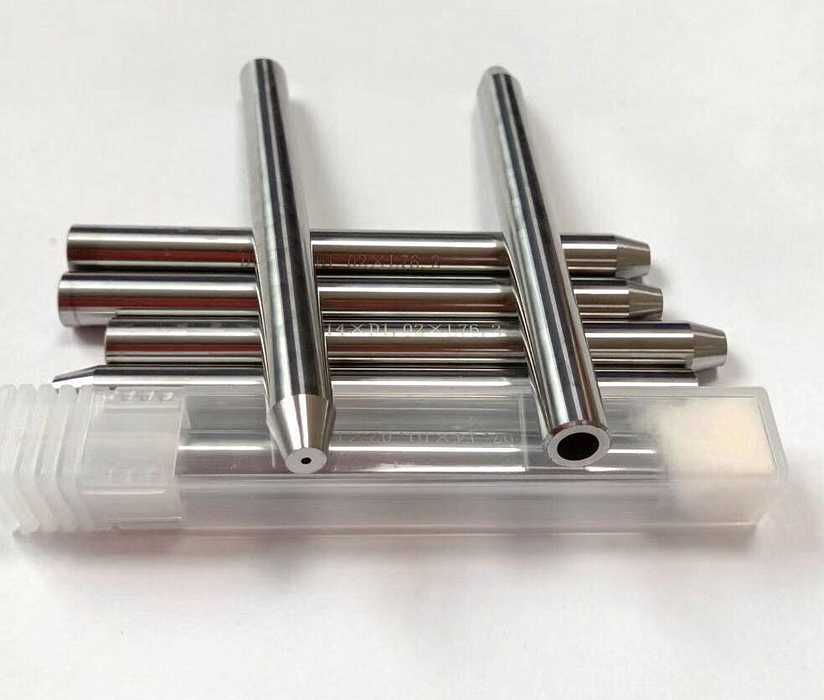
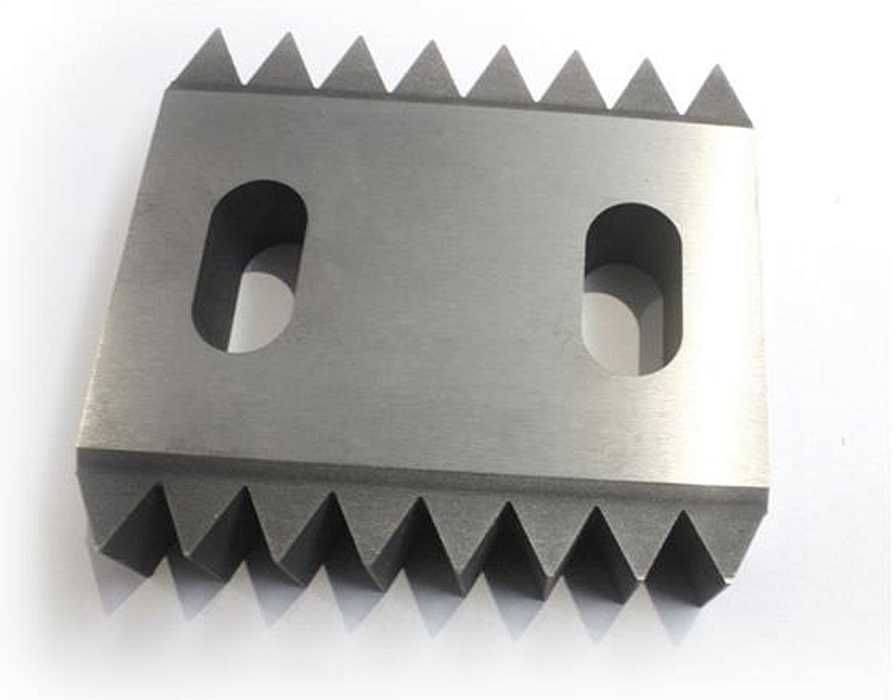
Products from tungsten-containing alloys
Properties:
-
High alloy density;
- High radiation resistance;
- High durability;
- High strength;
- Heat strength and heat resistance;
- Minimalcorrosionsensitivity;
- Available cost.
Application:
-
Parts for radioactivity logging devices;
- Storage vessels for radioactive agents;
- Protective shrouds;
- Collimators;
- Elements of non-destructive control hardware;
- Radiation-measuring and radiation control equipment etc.
Tungsten-copper
| Class | Composition (%), Cu | Composition (%), Impurities ≤ | Composition (%), W | Density, g/cm 3 ≥ | Hardness, НВ kgs/mm2 | Specific resistance, µΩ.cm ≤ | Flexural strength, MPa≥ |
| W50/Cu50 |
50±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
11.85 |
115 |
3.2 |
- |
| W55/Cu45 |
45±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
12.30 |
125 |
3.5 |
- |
| W60/Cu40 |
40±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
12.75 |
140 |
3.7 |
- |
| W65/Cu35 |
35±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
13.30 |
155 |
3.9 |
- |
| W70/Cu30 |
30±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
13.80 |
175 |
4.1 |
790 |
| W75/Cu25 |
25±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
14.50 |
195 |
4.5 |
885 |
| W80/Cu20 |
25±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
15.15 |
220 |
5.0 |
980 |
| W85/Cu15 |
15±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
15.90 |
240 |
5.0 |
1080 |
| W90/Cu10 |
10±2.0 |
0.5 |
base |
16.75 |
260 |
6.5 |
1160 |
Tungsten-nickel-iron
| Composition (%), Ni | Composition(%), Fe | Density, g/cm3≥ | |
| W90 |
7 |
3 |
16.85-17.25 |
| W92.5 |
5.25 |
2.25 |
17.15-17.85 |
Tungsten carbide
| Marking | Density, g/cm3 | Hardness, HRA | Flexural strength, MPa |
| YG6X |
14.8-15.1 |
≥91 |
≥1420 |
| YG6 |
14.7-15.1 |
≥89.5 |
≥1520 |
| YG8 |
14.6-14.9 |
≥89 |
≥1470 |
| YG8.2 |
14.4-15.0 |
≥88 |
≥1450 |
| YG8L |
14.6-15.0 |
≥89 |
≥1450 |
| YG15 |
13.9-14.2 |
≥86.5 |
≥2060 |
| HK12 |
14.2-14.7 |
≥87.5 |
≥2100 |
| KY10 |
14.1-14.5 |
≥87.5 |
≥2060 |
| YG20 |
13.4-13.8 |
≥83.5 |
≥2480 |
| YG20C |
13.4-13.8 |
≥82 |
≥2480 |
| YG20D |
13.4-13.8 |
≥82 |
≥2300 |
| YSN30 |
13.9-14.9 |
≥87 |
≥1900 |
Alternative ratio or tungsten carbide and cobalt is possible, when so requested by Customer.